Erosion Control Toolbox: Wire Mesh Confinement System
Introduction

Slopes steeper than 1:1 (H:V) will not reliably support vegetation and require a more permanent confinement technique than Rolled Erosion Control Products (RECP). A wire mesh confinement system provides additional shear strength necessary to hold non-vegetated fill material in place. Key features include:
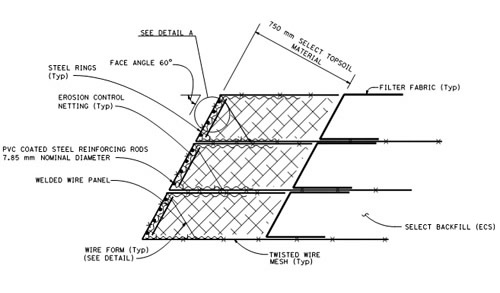
- Structural backfill material is placed in a double twisted wire mesh enclosure with an articulated front face that can be set to match the desired slope angle
- The bottom of the confinement system can function as a geosynthetic reinforcement layer which enhances slope stability
- Local Topsoil or select material is typically used at the slope to support sustainable vegetative growth
- Rolled Erosion Control Product (RECP) Netting is placed inside the confinement system to prevent release of topsoil through the face
- Welded Wire Confinement System is also known as Embankment Confinement System
When to Use This Treatment
- Fill or reconstructed cut slopes that are between 1.5:1 (H:V) and 0.5:1 (H:V).
- Coordinate the use of this treatment with the Division of Engineering Services (DES) Office of Geotechnical Services, which may prepare a Geotechnical Design Report for slopes greater than 2:1 (H:V)


Benefits
- Provides immediate slope reinforcement
- Creates slope breaks that shorten slope length and reduce runoff velocities
- Increases infiltration rates on dry sites
- Provides for vegetation establishment, cover, and natural recruitment
Limitations
- Unsuitable for slopes with limited equipment access
- Must have solid footing
Technical Design Tips
- Establishment of vegetation is difficult on slopes steeper than 1:1 (H:V), and extremely difficult on slopes that exceed 0.5:1 (H:V)
- Maximum slope gradient of 0.5:1 (H:V) has been used in extreme cases for slope tie-ins to natural grades
Consider Using With
To effectively treat sites with poor soils (compacted, sterile or poorly draining), consider combining this treatment with:
Plans and Details
- Nonstandard Detail - Erosion Control (Wire Mesh Confinement)
Updated: February 12, 2019

