Glossary
Jump to Term
- 3+ Carpool Lane
- Audible Pedestrian Signal
- Auxiliary Lane
- Bridge Scour
- Bicycle Lane Class IV
- Bicycle Lanes (Class I - IV)
- Bikepacking
- Capital Preventative Maintenance (CAP-M)
- Cast in Drilled Holes Piles (CIDH)
- Changeable Message Sign (CMS)
- Concurrency (Route)
- Crosswalk
- Curb Ramp, ADA Compliant
- Delineator
- Dig-outs
- Express Lane
- Fender, Bridge
- First Responders
- Fog Line
- Gabion Wall
- HOV Lane
- Leading Pedestrian Interval
- Managed Lane
- Lane Drop
- One-Way Traffic Control
- Open-graded Pavement
- Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon
- Permissive and Protected Left Turns
- Rectangular Rapidly Flashing Beacon (RRFB)
- Rock Slope Protection
- Roundabout
- Rubberized Asphalt
- Rumble Strips
- Sheet Piles
- Speed Feedback Sign
- Split Phase Traffic Signals
- State Highway Operational and Prevention Program (SHOPP)
- Storm Water Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) aka "Sweet Pea"
- Turn Pockets
- Throughput
- Traffic Bulb-outs
3+ Carpool Lane – A carpool lane requiring three or more passengers to travel toll-free.
Auxiliary Lane – An outer lane on the right side of a freeway that begins at an on-ramp and ends and the following off-ramp. The lane is a transition zone for cars entering the freeway and merging into the through-lanes.
Audible (Accessible) Pedestrian Signal - Creates a sound signal advising visually impaired pedestrians that it is safe to cross and intersection.

Bicycle Lane Class IV - Class IV Bikeways includes a barrier that separates cyclists or other users from motorized traffic. Types of barriers include grade separation, flexible posts, inflexible physical barriers, or on-street parking. The objective is to foster bicycling as a means of transportation, in a manner that improves safety for all users, including motorists, transit users, and pedestrians, including persons with disabilities.”
Bicycle Lanes (Classes I - IV)
- Class I: Paved, off-street paths completely separated from vehicle traffic.
- Class II: On-street, painted lane.
- Class III: Shared routes with traffic (no dedicated lane).
- Class IV: Separated bikeways with physical barriers.
Bikepacking - Backpacking by bicycle; taking a backpacking trip, but cycling rather than hiking
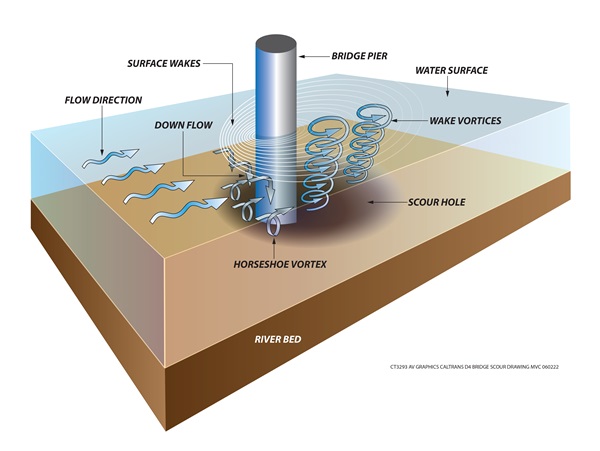
Bridge Scour - A process where rapidly flowing water strikes a bridge column resulting in whirlpools that erode the sediment supporting the bridge column, which can compromise the strength of the bridge.
Capital Preventative Maintenance (CAP-M) - Funding set aside to finance the repair of state highways when problems firs arise to avert more expensive repairs later.
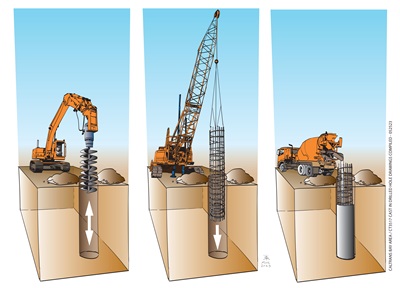
Cast in Drilled Holes Piles (CIDH) - Piles serve as a foundation for bridges and other structures. They can be driving into the ground by hammer (pile driving), vibrated into place, or cast in drilled holes. In the latter case, a cylindrical hole is bored into the ground. Next, a steel cages is inserted into the hole, and finally the hole is filled with concrete.
Changeable (Electronic) Message Sign (CMS) - An electronic informational sign facing traffic that displays messages which can be changed according to circumstances. There are permanent overhead CMSs and portable ones. Also known as electronic message board or sign. Shown below: A fixed changeable message sign and a portable changeable message sign.


Concurrency (Route) - A combination of at least two routes that share the same physical roadway. Such combinations occurs for geographic, economic or environmental reasons. Routes are often combined along rivers or through mountain passes. In less populated area routes are sometimes combined due to a decrease in traffic.
Crosswalk - A place designed for pedestrian to cross a road indicated with striping on the road. Typical state highway crosswalks come in three forms of striping, rectangular, continental and ladder. Below: a continental type crosswalk.

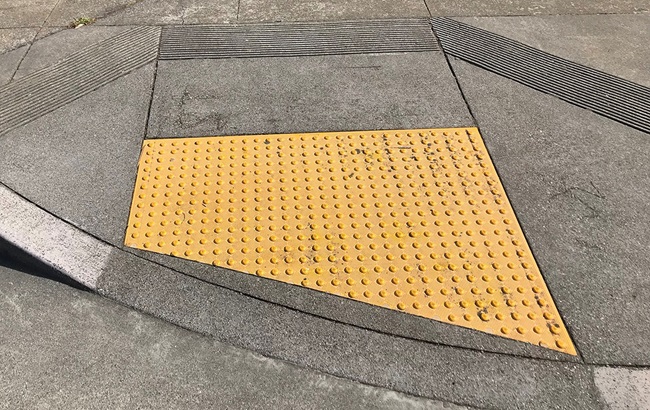
Curb Ramp, ADA Compliant - A place, typically at an intersection, where the sidewalk has been modified to slope down to the street to allow access for wheelchairs and covered with a yellow mat with bumps for the visually impaired. Compliant with the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990.

Delineator - A colored plastic tube, often orange or white, attached to a roadway, for the use of separating (aka delineating) lanes traffic. A channelizer is similar, but usually larger, and typically flat-faced, used for channeling traffic.

Dig-outs - A method of roadway repair where workers “dig out” layers of failed pavement and soil. The excavated areas are then refilled, compacted, and paved over.
Express Lane - A carpool lane that permits use by a single-occupancy vehicle upon payment of a toll. Also known as a HOT Lane, a high-occupancy toll lane.
Fender, Bridge - Unfortunately, it’s not just cars and trucks that collide with bridges. Sometimes, watercraft traveling below strike a bridge pier. To protect our bridges, Caltrans surrounds bridge piers with fenders that absorb the impact of wayward ships. Shown is the Bay Bridge with an adjacent barge repairing the fender after a ship strike.

First Responders - Firefighters, police, emergency medical technicians (EMT) who are called to the scene of an emergency to resolve the situation. Also known as emergency responders.
Fog Line - The solid white line, marking the outside edge of pavement, not including the shoulder.
Gabion wall - A retaining wall made of rock-filled steel cages. Gabion walls work well along streambeds and other aquatic locations but can be used elsewhere, too.

HOV Lane - High occupancy lane, also known as a carpool lane.
Leading Pedestrian Interval - Gives pedestrians the walk signal 3-7 seconds before vehicles are given the green light. It allows pedestrians a head start over right or left-turning traffic, establishing their presence – and visibility – in the crosswalk.
Managed Lane – A general term for either a carpool lane or an express lane. The term is often used during the project planning stage before deciding whether a lane would be a carpool lane or an express lane.
Lane Drop - A lane drop is a location on a highway where the number of lanes decreases. Lane drops can be categorized into three classes: lane exits, lane splits, and lane terminations. Reducing the number of lanes on a multi-lane roadway can reduce pedestrian crossing distances and slow vehicle speeds. Below is a merge signs indicating a forthcoming lane drop.

One-Way Traffic Control - A method of moving bi-direction traffic through a single lane by permitting a single direction of traffic to proceed while the opposing traffic waits. At some point the process is reversed, allowing the waiting traffic to proceed while traffic opposing traffic waits. Traffic is controlled by flaggers or traffic signals. Typically used in construction zones or roadways narrowed by landslides or flooding.
Open-graded Pavement - A type of pavement containing less sand and fine aggregate, resulting in a pavement with more air pockets or voids, places where water can drain, reducing sheeting and vehicle spray.
Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon - An electronic traffic signal operated by push button that stops vehicular traffic to allow pedestrian to cross a road. Often the signals are used at locations where there is a long distance between intersections where pedestrians typically cross the street. (See also Rectangular Rapidly Flashing Beacons)
![]()
Permissive and Protected Left Turns - When a motorist makes a left turn at a signalized intersection which lacks a left turn arrow, they are making a permissive left turn, in other words, making a turn when cross traffic is permits it. A motorist making left turn made at a signalized intersection with an illuminated green arrow is making a protected left turn, the green arrow means that cross traffic is stopped, meaning the motorist is protects by the traffic signal.
Rectangular Rapidly Flashing Beacon (RRFB) - A traffic control device installed at crosswalks to alert motorists of the presence of pedestrians, consisting of a pole, a sign, and flashing rectangular beacons activated by a push button. (See also Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon.)

Rock Slope Protection - A construction term describing the placement of rocks to bolster a slope and prevent erosion. Also referred to as riprap.

Roundabouts - A roundabout is an intersection where traffic travels around a central island in a counterclockwise direction. Vehicles entering or exiting the roundabout must yield to vehicles, bicyclists, and pedestrians.
 Roundabouts can have many advantages over traffic signals when constructed in the right location, including:
Roundabouts can have many advantages over traffic signals when constructed in the right location, including:
- They provide traffic calming, resulting in reduced speeds.
- They require less maintenance, have lower yearly operational costs, and have a longer service life.
- They reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reducing vehicle idling time.
- The median islands provide refuge for pedestrians, allowing them to cross one direction of traffic at a time.
- They provide additional opportunities for landscaping in the community.
Rubberized Asphalt - A type of pavement where rubber from recycled tires is added to the paving mix, creating a more durable asphalt that benefits the environment by diverting old tires from landfills.
RumbleStrips - Rumble strips are a road safety feature designed to alert drivers of potential hazards or changes in road conditions. They are raised or grooved  sections of pavement placed along the edges of roads or in the centerline. When a vehicle's tires travel over rumble strips, they produce a tactile and audible vibration or rumbling noise inside the vehicle, hence the name "rumble strips."
sections of pavement placed along the edges of roads or in the centerline. When a vehicle's tires travel over rumble strips, they produce a tactile and audible vibration or rumbling noise inside the vehicle, hence the name "rumble strips."
Sheet Piles - Unlike structural piles which are typically cylindrical in shape, sheet piles are usually elongated sheets of steel, which can be connected together by flanges, creating a wall. Sheet piles are often used to hold back earth, as in a retaining wall, or water, as in a coffer dam or seawall.

Speed Feedback Sign - A speed feedback sign, also known as a radar speed sign or dynamic speed display, is a traffic calming device used to alert drivers of their current speed and encourage them to adhere to the posted speed limit. These signs typically consist of a radar unit that detects the speed of approaching vehicles and a digital display that shows the detected speed to the driver.

Split Phase Traffic Signals - Split phasing describes an operation where all movements on one approach are served prior to all movements on the opposing approach. This is typically used if the geometry of the intersection, traffic volumes and/or crash history creates a conflict with normally non-conflicting movements.
State Highway Operational and Protection Program (SHOPP) - These are funds are used to make operational or maintenance improvements to the state highway, typically funding smaller projects to improve operations, for example, removing bottleneck or adding signalization; or maintaining highways by repaving, building retaining walls, etc. The credo "Fix it First," can be applied to SHOPP maintenance projects, as it's cheaper to fix smaller problems before they become larger issues.
Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans (SWPPP) - Stormwater runoff is water produced by rain or snowmelt that does not soak into the ground. Instead, it flows over land or impervious surfaces, such as paved streets and parking lots, picking up pollutants like trash, chemicals, oil, and dirt/sediment that harm rivers, streams, lakes, and coastal waters. To prevent such pollution, agencies develop plans called Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans. Such plans are often known by the nickname "Sweet Pea."
Turn Pockets - A special traffic lane used for making right or left turns.
Throughput – The number of vehicles or persons passing through a lane or road over a specific period, usually an hour or a day. Vehicle throughput is the number of vehicles traveling through a location. Person throughput is the number of people traveling through a location.
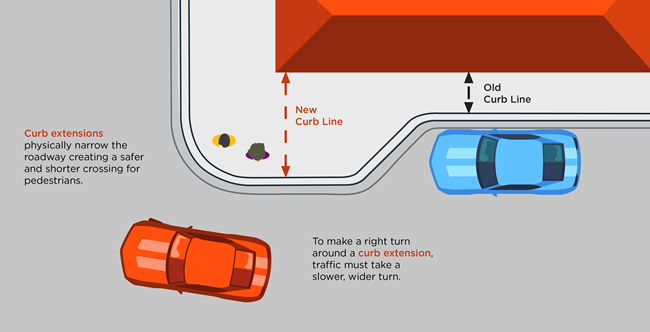
Traffic Bulb-outs – An extension of the sidewalk and curb at an intersection that shortens pedestrians' crossing distance and slows down turning vehicles. Also known as a curb extension.